Have you ever thought about the impact of ergonomics on your daily work life? Ergonomics has a significant impact on your health, comfort, and productivity at the office.
Ergonomic errors, such as poor posture, an unsuitable chair, or incorrect screen positioning, can lead to physical pain, increased fatigue, and decreased concentration over time.
Understanding ergonomic errors and correcting them is therefore an important step in improving your well-being at the office.
What is an ergonomic problem?
An ergonomics problem arises when a workstation is ill-suited to the user's physical and cognitive needs. By designing an ergonomic workstation, we aim to optimize employee comfort and efficiency while minimizing the risk of injury or musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
Why is poor ergonomics a problem?
Poor ergonomics in the office can have a significant impact on employee health and well-being. Indeed, prolonged poor posture can lead to back, shoulder, neck, and wrist pain, as well as chronic conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
In addition to physical impacts, ergonomic problems at work can reduce concentration and productivity, thus increasing errors and fatigue. It is therefore essential to create an ergonomic workstation, whether in office spaces or for remote work.
The most common ergonomic mistakes in the office
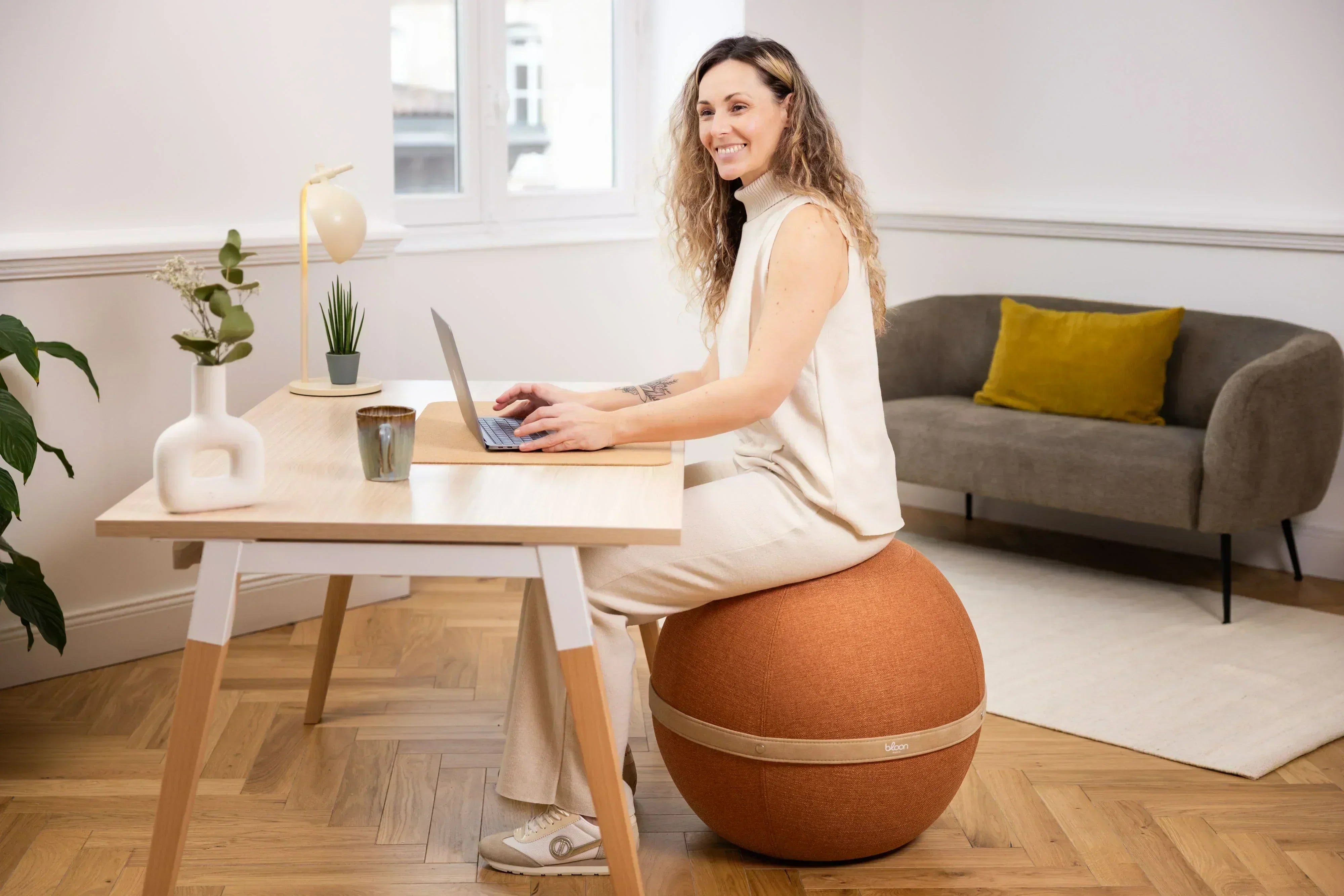
Poor sitting posture
Poor posture, such as a hunched or overly rigid back, is a major source of ergonomic problems in the workplace. This can lead to lower back pain and muscle tension.
In France, approximately 70% of employees report having experienced back pain related to poor posture at work, and nearly 3 million workdays are lost each year due to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
That is why it is important to adopt healthy work habits and invest in appropriate ergonomic solutions.
Solutions:
-
Use a suitable ergonomic chair.
-
Learn to maintain good posture.
-
Reduce tension by alternating between sitting and standing postures.
Desk and screen height incorrectly adjusted
A poorly positioned screen, whether too high or too low, can cause neck pain and tension. An incorrect setup can lead to increased discomfort in the neck and shoulders, making prolonged work difficult and painful. Studies show that nearly 70% of employees suffer from pain related to poor screen positioning, directly impacting their productivity and well-being at work. Therefore, properly adjusting the height and angle of the screen is essential to promote a healthy and comfortable posture.
Solutions:
-
Position the screen at eye level, 50-70 cm from the face.
-
Adjust the desk height so that your elbows are at a 90° angle when seated, in accordance with ergonomic guidelines. a well-organized workstation .
Inappropriate or poorly adjusted seat
A non-ergonomic or poorly adjusted chair is a common cause of back pain, particularly in the lumbar region. The lack of proper support can lead to increased strain on the spine, causing chronic or acute pain.
Furthermore, an incorrect seat height adjustment can prevent the feet from touching the ground or, conversely, cause the knees to bend excessively, which disrupts blood circulation.
In the long term, these inadequate postures worsen ergonomic problems and contribute to a decrease in comfort and productivity.
Solutions:
-
Choosing a suitable ergonomic seat the Bloon balloon seat.
-
Adjust its height to allow for optimal alignment with the desk.
Arms and wrists incorrectly positioned
Incorrect arm and wrist positioning during gripping can have serious health consequences.
According to a study , approximately 60% of office workers suffer from pain related to poor posture, and among them, nearly 10% develop musculoskeletal disorders such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
This syndrome, caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist, can lead to pain, numbness, or even loss of strength in the hand.
These problems are often aggravated by prolonged use of a keyboard or mouse without adequate arm and wrist support.
Solutions:
-
Position the keyboard at the correct height with straight wrists.
-
Use an ergonomic wrist rest and an ergonomic mouse to limit tensions.
-
Maintain a natural posture of the arms and wrists.
Lack of movement and prolonged static posture
Sitting for too long promotes musculoskeletal disorders and muscle stiffness. These ergonomic problems are particularly prevalent when working remotely. When the body remains in a static posture for extended periods, muscles and joints experience excessive strain, which can lead to chronic pain.
Solutions:
-
Take regular breaks every hour.
-
Alternate positions with a sit-stand desk.
-
Realize light exercises and stretching to alleviate muscle tension.
Inadequate lighting
According to recent studies, approximately 50 to 90% of office workers report experiencing some form of Eye strain , often linked to inadequate lighting or prolonged exposure to screens.
Poor lighting can lead to headaches, blurred vision, or eye strain, exacerbating ergonomic problems in the workplace. These symptoms not only reduce visual comfort but also daily productivity and concentration.
Solutions:
-
Use soft natural lighting as much as possible.
-
Install adjustable lamps to avoid reflections.
-
Reduce exposure to blue light with screen filters.
FAQ: All about ergonomics problems in the office
What is an ergonomic problem?
An ergonomic problem occurs when the work environment, tools, or postures adopted create discomfort or health risks. This can cause physical pain, fatigue, or decreased productivity.
What are the 7 ergonomic risk factors?
The main ergonomic risk factors are:
-
Uncomfortable or prolonged postures.
-
Repetitive movements.
-
Excessive force applied.
-
Vibes.
-
Localized pressures.
-
Extreme temperatures.
-
Inadequate lighting.
What are the ergonomic constraints?
Ergonomic constraints include physical aspects (postures, repetitive movements), organizational aspects (schedules, work pace) and environmental aspects (lighting, noise, temperature).
What are the 3 types of ergonomics?
The 3 types of ergonomics:
-
Physical ergonomics: Focused on the human body and its biomechanics.
-
Cognitive ergonomics: Concerning mental processes, such as concentration or decision-making.
-
Organizational ergonomics: Focused on work systems and methods.
What is ergonomics in the workplace?
Ergonomics in the workplace involves adapting the workstation, tools, and work environment to the employee's abilities and needs, in order to prevent injuries and optimize performance.
What are the three pillars of ergonomics?
The three PSs of ergonomics are: Physical, cognitive, and organizational ergonomics. Cognitive ergonomics.
How to improve the ergonomics of the workstation?
To improve the ergonomics of the workstation:
-
Adopt a correct posture with good back support.
-
Adjust the screen height to avoid neck strain.
-
Use an ergonomic and adjustable chair.
-
Take regular breaks to move around and rest your eyes.
What ergonomic factors have a negative impact on a person's well-being?
Static postures, poor lighting, unsuitable tools, or stress related to unhealthy work rhythms can all harm well-being.
How to have an ergonomic office?
-
Optimize the desk layout for a natural posture.
-
Reduce glare by adjusting the lighting.
-
Choose ergonomic equipment such as suitable keyboards and mice.
What constitutes good ergonomics?
Good ergonomics integrates comfort, safety and efficiency to prevent injuries and improve the quality of working life.
What does office ergonomics primarily aim to reduce?
Office ergonomics primarily aims to reduce musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and physical or mental fatigue related to poor working conditions.
What are the limits of ergonomics?
The limitations of ergonomics can include the cost of ergonomic equipment, resistance to change, or a lack of awareness among employees and employers.
What are the tools of ergonomics?
Ergonomic tools include ergonomic chairs, sit-stand desks, monitor stands, ergonomic keyboards and mice, and footrest mats.
Why is ergonomics in the office important?
Office ergonomics is important because it prevents pain, improves employee well-being, and promotes better productivity and job satisfaction.
Finally, if you try to correct your ergonomic errors by taking into account our solutions and advice, it is possible to significantly reduce your ergonomic problems at work, whether in the office or teleworking.