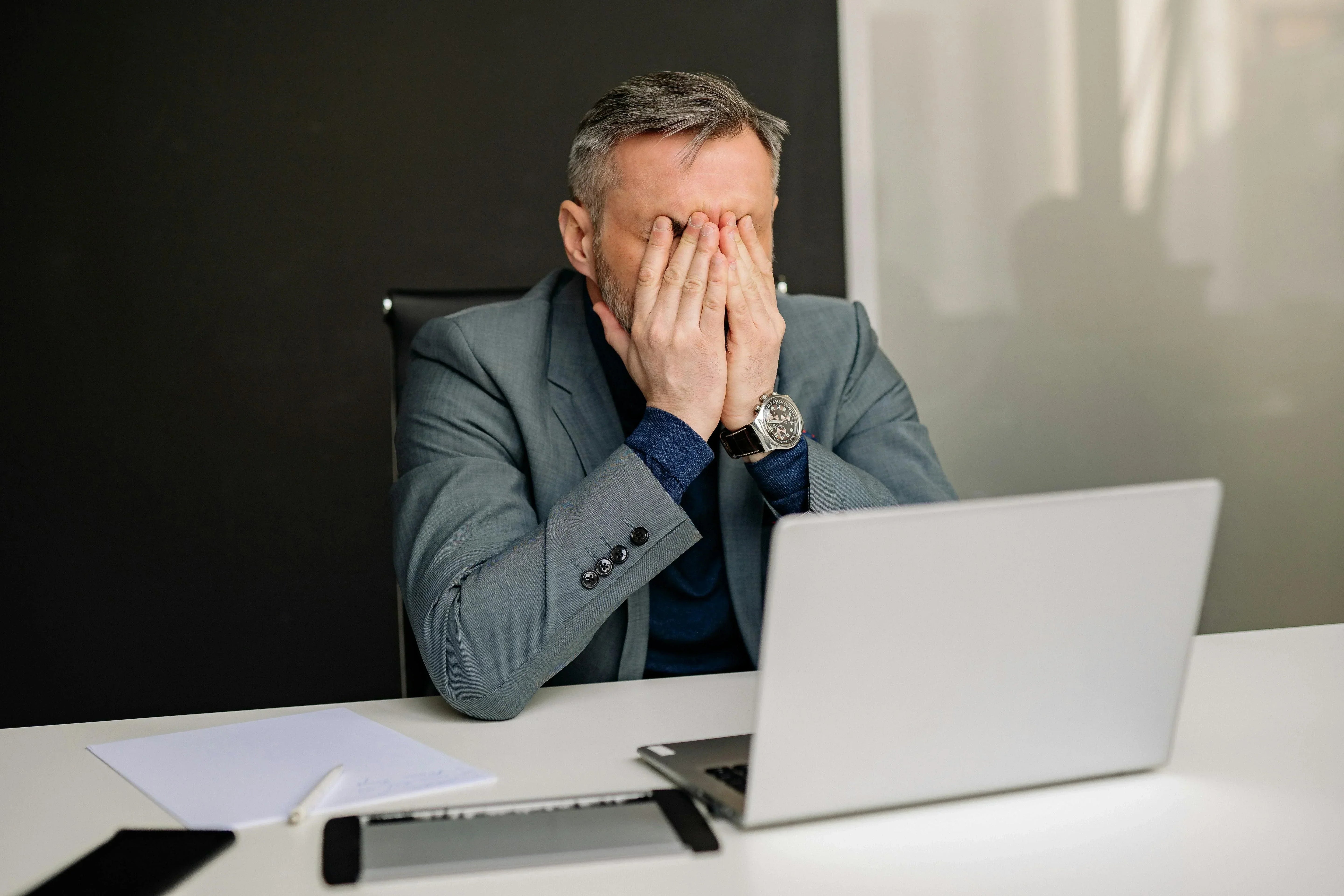
We often talk about physical health, but what about mental health at work?
According to the Paris GHU, 47% of employees have already been forced to work less or less efficiently due to their mental health.
In this article, we explain what mental health at work is, the factors that impact it, and the warning signs you shouldn't ignore. We also provide tips for maintaining your mental health.
What is mental health at work?
Definition according to WHO
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , mental health is a state of well-being in which a person can achieve their potential, cope with normal life stresses, work productively and contribute to their community.
In the workplace, mental health at work is defined by the absence of psychological disorders, but also by the ability of workers to thrive. An employee who is fulfilled at work is better able to manage periods of heavy workload while maintaining personal balance.
Difference between mental health and well-being at work
Mental health and well-being at work are two related, but different, concepts.
Mental health refers to an individual's psychological and emotional balance, including the prevention of disorders such as anxiety or depression.
Well-being, on the other hand, refers to a broader spectrum including professional satisfaction, personal development and physical comfort in the work environment.
For example, a company may offer ergonomic offices to improve well-being, but this does not guarantee optimal mental health if the workload remains excessive.
Factors that impact mental health at work
The pressure of results


Too much workload and constant pressure to achieve ambitious goals are the main factors that affect mental health at work.
According to a survey, 61% of employees today report experiencing work-related stress in their current role.
For example, unrealistic deadlines or excessive workloads can lead to mental exhaustion and even depression. Therefore, it is important for companies to regularly assess the workloads placed on their employees.
Lack of support
A work environment lacking mutual support and mutual assistance from managers and/or colleagues can quickly impact mental health at work. Employees deprived of adequate support risk feeling isolated or overwhelmed. For example, an employee faced with critical unforeseen events without reassuring guidance will be more prone to anxiety, a symptom often linked to poorly managed work situations.
Conflicts and harassment
Tensions between colleagues and harassment can seriously impact mental health at work. For example, degrading remarks or repeated exclusion can lead to depression.
According to the World Health Organization , depression and anxiety are estimated to cause an estimated 12 billion lost working days each year, representing a loss of productivity of $1 trillion annually.
Lack of autonomy
Lack of autonomy in professional decision-making is another factor that significantly impacts mental health at work. When an employee is constantly micromanaged or their role lacks clarity, it can lead to frustration and significant stress.
For example, an employee faced with rigid constraints and little involved in their own professional choices risks feeling increasing discomfort.
A stressful work environment
A cluttered, noisy work environment with unoptimized lighting is particularly anxiety-inducing.
A survey conducted in France reveals that around 30% of workers admit to not being able to stay focused for more than an hour without interruption.
The increase in distractions, for example, in an open-plan office can reduce productivity and affect mental health at work.
Mental health warning signs you shouldn't ignore
Emotional and behavioral disorders
The first warning signs of an employee in mental distress are, for example, an employee who reacts sharply to the slightest annoyance or who appears anxious.


These emotional and behavioral disorders can also be accompanied by signs such as a tendency to isolate.
Decreased motivation
A sudden drop in motivation, which is seen as a lack of interest in the tasks to be performed, is a warning sign that should not be ignored.
This condition can be aggravated by lack of recognition or tension.
Sleep disorders
Problems such as insomnia or nighttime awakenings are clear signals of increased stress.
Lack of sleep combined with intense pressure diminishes an employee's ability to manage work responsibilities and concentrate.
Risk of depression
Depression is a serious consequence of mental health problems at work. It can manifest as a loss of energy, feelings of worthlessness, or persistent negative thoughts, requiring prompt treatment.
Risk of burnout
Another dramatic consequence of mental health problems at work is burnout. This professional exhaustion occurs when the emotional burden and tensions at work are too intense. The lack of recovery space exacerbates the risk. Burnout is characterized by profound fatigue, loss of motivation, and increasing detachment.


How to protect the mental health of your employees?
Better manage your time and priorities
Effective time management is essential to maintaining mental health at work.
Using tools like to-do lists or digital calendars helps structure your day and prioritize emergencies.
It is crucial to learn to delegate when necessary and not to set unrealistic goals for yourself.
Take breaks and disconnect
Regular breaks help you replenish your energy and maintain optimal productivity.
Taking time out from screens and work also promotes mental well-being and prevents burnout.
Communicate with colleagues or your manager

Communicating clearly with your team or manager helps resolve problems and reduce stress. Open communication allows you to express your needs, clarify expectations, and, if necessary, request appropriate support.
Setting boundaries between professional and personal life
Maintaining a clear separation between work and private life is essential.
Setting specific schedules and respecting these limits helps maintain a healthy balance and reduce the risk of overwork.
Practice regular physical activity
Regular physical activity is a great way to release built-up pressure.
Regular physical activity, such as walking, yoga, or swimming, strengthens not only the body but also the mind, helping to release endorphins, the happy hormones.
Creating social bonds at work
Fostering positive relationships with colleagues helps you feel supported and integrated into your professional environment. Social moments, such as coffee breaks or team lunches, strengthen collective well-being.
Optimizing your work environment
A well-organized and ergonomic workspace improves concentration and reduces stress.


Personalizing your space with calming elements, such as plants or photos, can also promote a climate of serenity.
The role of employers in mental health at work
Create a culture of kindness and listening
Employers must foster a work environment based on respect and attentiveness. A culture of caring fosters greater team cohesion and helps prevent the onset of stress-related disorders.
Train managers to detect weak signals
Managers play a key role in detecting the first signs of distress among their employees.
Training them to recognize these weak signals allows them to intervene quickly and prevent more serious situations.
Establish psychological support systems
Providing access to support services, such as psychologists or crisis lines, can help employees overcome their difficulties.


These measures show that the company cares about the well-being of its employees.
Encourage work-life balance
Employers should promote policies that allow for a healthy separation between work and private life. This may include flexible schedules, teleworking, or implementing a right to disconnect.
In conclusion, mental health at work is a priority for any company whose goals are the productivity and professional development of its employees. By cultivating a positive work environment, employers build a more sustainable and successful business.