The legal responsibility of employers in ergonomics at work corresponds to the obligation to ensure safe working conditions adapted to the needs of their employees.
In France, Article L4121-1 of the Labor Code requires employers to take the necessary measures to guarantee the safety and protect the physical and mental health of workers.
Ergonomics at work , directly linked to this obligation, remains a fundamental element in reducing and minimizing risks at work. Legislation concerning ergonomics at work lays a solid foundation for action in favor of a healthy working environment.
Consider ergonomics from the design stage of workstations
According to Article R4214-12 of the French Labor Code , the layout of workstations is the direct responsibility of the employer. The employer must ensure the physical and mental safety of employees.
Anticipating ergonomic needs in layouts
Article R4225-1 of the French Labor Code states that workplaces must be designed to protect employee health. When setting up workstations, employers must take ergonomic principles into account to prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and improve employee well-being.
Employers must provide workspaces that comply with ergonomic regulations.

Best practices to avoid costly retrofits
Taking ergonomics into account and investing in ergonomic furniture when designing workstations helps limit costly future adjustments and the risk of accidents due to poor ergonomics at work.
Employers must prioritize their ergonomics initiatives.
Analysis of risks related to ergonomics at work
According to Articles R4121-2 et seq., the employer must also ensure that the ergonomic risk analysis is carried out and updated regularly. This proactive approach helps prevent work-related disorders and ensures employee safety.
Identify risk factors
As part of an occupational risk assessment provided for by decree no. 2001-1016, an employer is responsible for identifying ergonomic risk factors, such as poor posture, repetitive movements or excessive effort.
Analysis of these elements allows the development of specific solutions to reduce physical constraints.
Analysis of the work environment
Lighting, noise, temperature, desk, office chair and even the organization of workspaces are among the elements to be analyzed to ensure that ergonomic standards are respected.
The employer, in accordance with ergonomic legislation at work , is required to analyze the work environment.
Implement ergonomic prevention measures
Adapting workstations
Under Article L4121-2 of the French Labor Code , employers must adapt workstations to the physical characteristics of employees. These adaptations help minimize unnecessary effort and improve employees' posture, directly meeting the requirements of workplace ergonomics legislation .
Provide ergonomic equipment
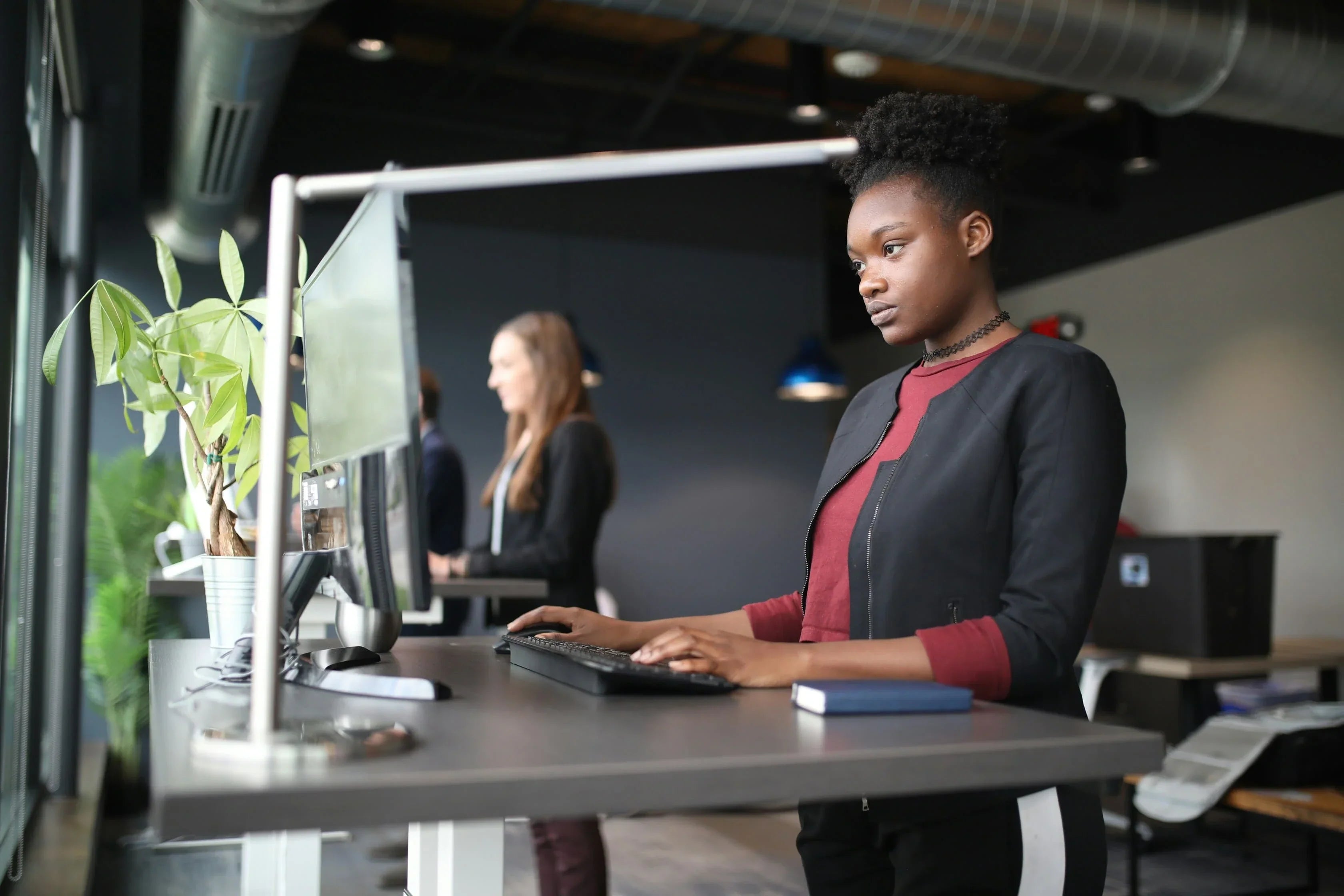
The employer is required to provide ergonomic furniture and accessories that meet regulations and the needs of employees.
Ergonomic equipment may include an ergonomic office chair for posture, a sit-stand desk, a monitor stand, and an ergonomic mouse or keyboard.

Reorganize tasks and work rhythms
Employers must organize tasks and work rhythms efficiently to avoid physical or mental health risks for employees. Work organization includes alternating tasks and regular breaks.
Inform and train workers in ergonomics
The employer has a duty to raise awareness and inform employees about ergonomics and to facilitate their adherence to new ergonomic measures.

Regulations on employee information
Article L4141-2 specifies that the employer must inform and train workers on the risks arising from work and poor ergonomics.
This includes dedicated sessions on ergonomics at work during which employees are informed about the physical and mental risks linked to ergonomics.
Important information
According to Article R4141-3 , safety training must enable employees to ensure their own safety and that of workers around them.
The correct use of work equipment, good posture and habits to adopt at work are important information that employees must know to reduce the risk of accidents and improve productivity, well-being and performance at work.
Sanctions for non-compliance with the ergonomics obligation
Civil penalty
An employer who fails to comply with ergonomics regulations may be held civilly liable for failing to provide a healthy working environment. This is rooted in the general liability defined by the French Labor Code.
The employer risks fines of up to €10,000 per employee concerned, or even more depending on the seriousness of the facts or in the event of a repeat offense.
Criminal penalty
Failure to comply with ergonomic legislation at work can also lead to criminal sanctions, in the event of endangerment or serious negligence.
Suspended prison sentences and heavier financial penalties may be imposed if an employee's health has been clearly endangered.
FAQ: Employers in workplace ergonomics
What are an employer's responsibilities in terms of ergonomics?
The employer's responsibilities in terms of ergonomics are the analysis, prevention and evaluation of ergonomic risks for its employees.
Who is responsible for ergonomics at work?
The employer is responsible for implementing ergonomics at work.
What are the employer's duties?
The employer's main duties in terms of ergonomics include the layout of workstations, the provision of suitable equipment, and the organization of work.