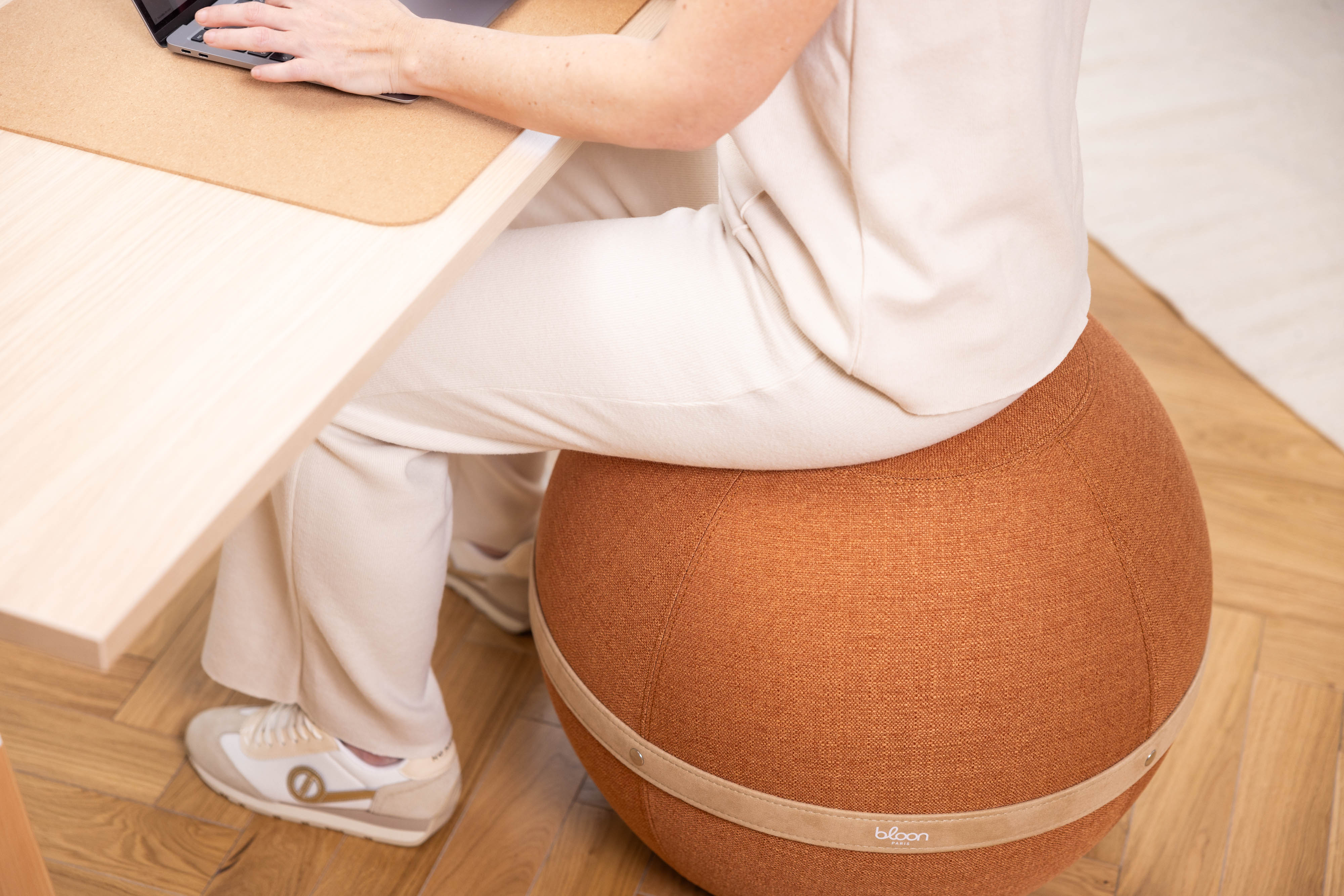
Your movements and postures at work have a significant impact on your health and well-being. That's why, to prevent back pain and musculoskeletal problems, you must adopt good habits by adopting good posture, setting up an ergonomic workstation, and incorporating exercise into your routine.
Consequences of poor posture at work
Health consequences
Poor posture and movement at work can have a negative impact on your health. These adverse health consequences include chronic back, shoulder, and neck pain, which can develop into musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) such as tendonitis, lower back pain, and neck pain. Poor posture and movement at work can also lead to increased fatigue and decreased energy.
Impact on productivity and general well-being
Poor posture and posture at work also impact productivity and overall well-being. Pain can affect employees' productivity and overall well-being. Fatigue leads to a loss of concentration and efficiency, as well as stress and decreased motivation. In the long term, this can lead to a general feeling of dissatisfaction and a decline in the quality of professional and personal life.
Gestures and postures at work
The basics of good posture
Adopting correct posture is important for preventing musculoskeletal pain and disorders. Good posture involves keeping your spine properly aligned, keeping your head straight, shoulders back, and your lower back slightly arched. Imagine a straight line running from your ears to your shoulders, then to your hips and knees. Your feet should be flat on the floor or on a footrest, with your knees at a 90-degree angle, and avoid crossing your legs. Your arms should be close to your body, with your elbows at a 90-degree angle or slightly greater, and your wrists should remain straight, without bending or twisting.

Sitting posture
To maintain good sitting posture, you need to set up your workstation properly. To start, your office chair or armchair should properly support your back and allow your feet to be flat on the floor and your knees to be at hip height. If your feet don't touch the floor, you can use a footrest. Next, your computer screen should be positioned at eye level, about an arm's length away, so you don't have to look down or up to look at your screen and avoid damaging your eyes.
Standing posture
When working in a sitting position for long hours, take breaks to alternate between sitting and standing positions. You can also opt for a sit-stand desk. When working standing, using anti-fatigue mats can reduce pressure on your feet and legs. To relieve leg pressure, we recommend changing positions regularly and performing light movements, such as rocking from one foot to the other, which helps improve blood circulation.
Posture and gestures for lifting heavy loads
If you have to lift heavy loads at work, you must adopt proper lifting techniques to avoid injury. Use your leg strength, not your back, to lift objects. Keep your knees straight and bend as if you were squatting. Keep the load close to your body to reduce stress on your back. Use assistive equipment such as hand trucks and trolleys to carry heavy loads.
If you would like to learn more about good posture in everyday life, check out our article: How to Adopt Good Posture in Every Day.
Solutions to prevent pain
Workstation ergonomics
To adopt good gestures and posture at work, having an ergonomic workstation is essential. A good workspace layout should allow easy and comfortable access to all necessary equipment. You should position your keyboard, mouse, and phone so that you don't have to stretch your arms or bend uncomfortably to reach them. You can use ergonomic accessories such as lumbar support for your chair, a wrist rest for your keyboard and mouse, and adjust the height of your screen so that it's at eye level to naturally maintain good posture.
Exercises and stretches at work
Here are 2 simple stretches to do during breaks:
Neck stretch
Sit with your back straight and your feet flat on the floor. Gently tilt your head toward your right shoulder and hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds. Repeat on the other side. This will help relieve tension in your neck and shoulders.
Back stretch
In a seated position, place your hands behind your head and slowly lean forward, slightly rounding your back. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds. This stretch helps loosen back muscles and improve flexibility.
Exercises to strengthen the back and neck
- Back Extension : Lie on your stomach with your arms at your sides. Slowly lift your head, shoulders, and chest off the floor while keeping your feet firmly planted. Hold this position for 5 to 10 seconds, then return to the starting position. Repeat this exercise 10 times. This exercise strengthens your lower back muscles.
- Scapular Retraction : While sitting or standing, squeeze your shoulder blades together as if you were trying to hold a pencil between them. Hold this position for 5 to 10 seconds, then release. Repeat this exercise 10 to 15 times. This exercise strengthens your upper back muscles and improves shoulder posture.
- Relaxation and breathing techniques : Incorporating relaxation and breathing exercises into your routine can help reduce pain and relax you. You can practice deep breathing at your office or home. Inhale through your nose, filling your lungs, then exhale slowly through your mouth, emptying your lungs. Repeat 5 to 10 times to reduce stress and tension.
If you'd like more exercises for back pain, stress, and staying active at the office, check out our article: 10 Exercises with a Ball at the Office: For an Active and Balanced Life.
Ultimately, maintaining your health at work is as simple as adopting good posture, incorporating stretching and muscle strengthening exercises into your routine, staying active, and having an ergonomic workstation if you work in an office.